Pixyl.Neuro.MS
AI solution to support diagnosis and monitoring of multiple sclerosis (MS)
Pixyl.Neuro.MS automatically analyses MRI images in few minutes, providing access to quantified measures of lesion volume and brain atrophy and longitudinal follow-up.
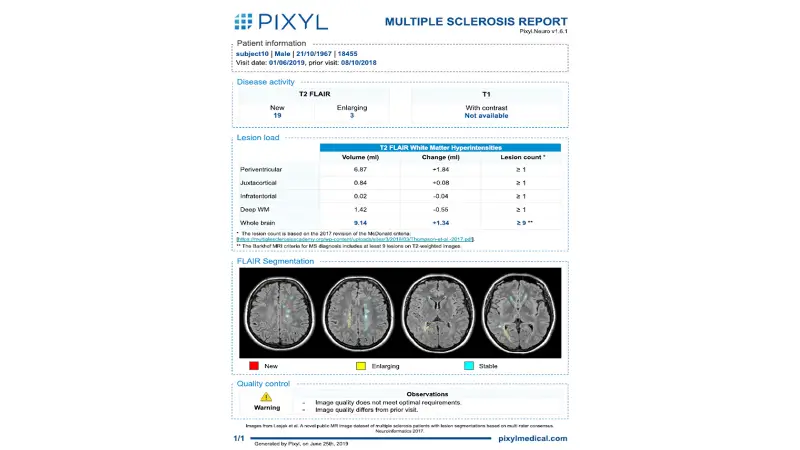
Automatic detection, quantification and characterization of lesions in anatomical areas of interest
Longitudinal analysis of disease evolution if prior exam available
"Active (new or enlarging) T2 Flair lesion volume count and volume. T2 Flair lesion volume and count, classified by region of interest. "
Automated production of a structured report and a segmented series (lesion outline) directly in the PACS
Save time by fully automating time-consuming tasks such as counting lesions or comparing with prior exam
Reduce variability in intra- and inter-operator measurements, and standardize patient monitoring
Integrate AI support directly into your existing infrastructure and regular clinical workflow
Save time, secure your diagnosis and optimize your workflow with Incepto
Publications
-
Thomas Mistral, Pauline Roca, Christophe Maggia, Alan Tucholka, Florence Forbes, Senan Doyle, Alexandre Krainik, Damien Galanaud, Emmanuelle Schmitt, Stéphane Kremer, Adrian Kastler, Irène Troprès, Emmanuel L. Barbier, Jean-François Payen, and Michel Dojat. “Automated quantification of brain lesion volume from post-trauma MR diffusion-weighted Images.” Frontiers in Neurology, 2022.
-
Bonnan M, Money P, Desblache P, Marasescu R, Puvilland LM, Demasles S, Dahan C, Krim E, Tucholka A, Doyle S, Barroso B. Focal cortical atrophy following transient meningeal enhancement in a progressive multiple sclerosis. Neurol Sci. 2021 May;42(5):1959-1961.
-
Pauline Roca, Arnaud Attyé, Lucie Colas, Alan Tucholka, Pascal Rubini, Stenzel Cackowski, Juliette Ding, Jean-François Budzik, Felix Renard, Senan Doyle, Emmanuel L. Barbier, Imad Bousaid, Romain Casey, Sandra Vukusic, Nathalie Lassau, Sébastien Verclytte, and François Cotton. “Artificial intelligence to predict clinical disability status scale score in patients with multiple sclerosis using FLAIR MRI” Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging 2020.
Regulatory
Contact us to know if this product is available in your country.

