Coreline Aview LCS+
AI solution for lung nodule detection and management, CAC and emphysema on chest CT scans
Coreline's AVIEW LCS Plus provides integrated detection and fully automatic analysis of *Big 3 diseases from a single examination. It automatically generates a pulmonary nodule readout for lung cancer diagnosis and quantifies the quantitative results of emphysema and coronary artery calcification. It is the Solution that can detect three diseases at the same time through low-dose chest CT image with CT kernel conversion AI technology.
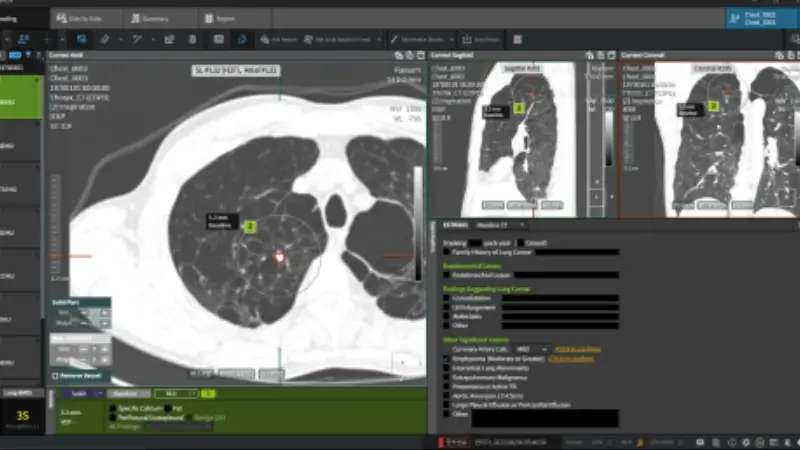
LCS - Lung Cancer Screening
It automatically identifies lung nodules—even tiny ones—and classifies them (e.g., solid, part-solid, non-solid), measuring their size, volume (3D), morphology, and location.
COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The system analyzes low-dose chest CT scans to quantify emphysema using metrics such as the low attenuation area (LAA) and generates an emphysema index.
CAC - Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring
Automated calcium detection: Identifies calcifications in coronary arteries from low-dose CT scans and computes calcium scores (e.g., Agatston, volume, and mass scores).
Segment-level analysis: Performs segmentation of major coronary arteries (e.g., LM, LAD, LCX, RCA) to provide detailed scoring.
Comprehensive Multi-Disease Screening
Automated, Standardized, and Efficient Reporting
Enhanced Patient Management & Risk Stratification
Save time, secure your diagnosis and optimize your workflow with Incepto
Publications
-
Automated CAC & Emphysema Predict Outcomes in Lung Cancer Screening
Title: Automated Coronary Artery Calcium and Quantitative Emphysema in Lung Cancer Screening: Association With Mortality, Lung Cancer Incidence, and Airflow Obstruction
Journal: Journal of Thoracic Imaging (2023)
Summary: In a 6-year follow-up of 4,098 participants undergoing low-dose CT screening, AVIEW LCS PLUS automatically quantified CAC (Agatston calcium scores) and emphysema (LAA). The study demonstrated strong associations between these imaging biomarkers and risk of mortality, lung cancer incidence, and airflow obstruction, highlighting their value for risk stratification. -
"Ground-Truth Validation of Nodule Detection & Volumetry
Title: Absolute ground truth-based validation of computer-aided nodule detection and volumetry in low-dose CT imaging
Journal: European Journal of Medical Physics (2024)
Summary: Using a meticulously constructed anthropomorphic phantom with 3D-printed nodules of known sizes and morphologies, this study rigorously tested AVIEW LCS+ across different CT doses and reconstruction algorithms. It confirmed high detection sensitivity (≥ 83%) and precision (≤ 10% volumetric error for nodules > 6 mm), irrespective of imaging parameters—demonstrating robustness for low-dose lung CT environments." -
AI as a First-Reader for Lung Cancer Screening
Title: Feasibility of AI as first reader in the 4-IN-THE-LUNG-RUN lung cancer screening trial: impact on negative-misclassifications and clinical referral rate
Journal: European Journal of Cancer (2024), published as a News digest in January 2025
Summary: This study assessed whether AVIEW LCS (v1.1.42.92) could serve as an effective first-line reader in the 4-IN-THE-LUNG-RUN trial. It measured how AI performance impacted misclassification of negative cases and referral rates. The results showcased AI’s capacity to reliably triage negative scans—pointing toward reduced radiologist workload without sacrificing accuracy. -
(*) Dr Catherine Jones (Monash University, University of Sydney and I-MED Radiology Network, Australia - 130 chest scans
Analsye of the impact of AI on radiologists' reading time and estimated return on investment (ROI) + CLAIM = Time savings(*), up to
-60% reading time
Regulatory
Contact us to know if this product is available in your country.

