qXR
AI solution for the diagnosis of chest x-rays
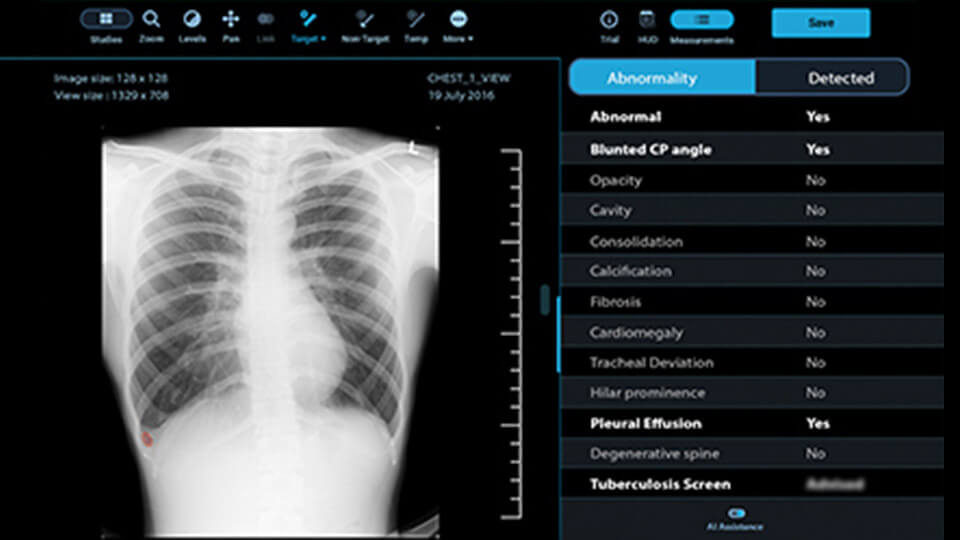
qXR™ is a tool assisting radiologists and emergency services in the detection of thoracic pathologies in radiography. qXR™ analyses the radiograph, detects numerous thoracic pathologies (lung, pleura and mediastinum) and integrates the result into the radiologist’s usual reading environment.
A work list with the classification of examinations as “normal” and “abnormal” enables radiologists and emergency physicians to prioritise the flow of patients through the emergency department.
Automatic detection and localization of thoracic pathologies on the lung, pleura and mediastinum
For example, the qXR solution detects opacities such as cavities, cardiomegaly, effusions, pneumothorax … The solution also allows screening for tuberculosis and COVID 19.
Automatic classification and sorting of exams as normal / abnormal within a work list
The qXR algorithm offers radiologists and emergency physicians a comprehensive overview of the AI results of all exams of the day with normal / abnormal triage.
Automated production of a report incorporating an annotated image and detected and localized pathologies
qXR generates a pre-filled report that contains the annotated images, information on the normal / abnormal nature of the exam and any anomalies detected and their localization.
- chest pathologies
- lung
- pleura
- mediastinum
- opacitities
- pneumothorax
- effusions
- x-ray
Save time, reassure your diagnosis and streamline your workflow with Incepto

Qure.ai was founded in 2016 by an Indian team whose founders came from the Georgia Institute of Technology and the Max Planck Research Institute. The company’s mission is to use artificial intelligence to make healthcare more accessible and affordable. Their team combines unique expertise in data science with clinical and scientific knowledge, which has already enabled them to publish in major scientific journals such as the Lancet and Radiology. Very active and recognised in global tuberculosis screening programmes, they are committed to designing concrete solutions to a range of clinical questions.
Publications
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation.Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation: UNSCEAR 2008 Report. Vol 1. New York, NY: United Nations; 2010.
- Forrest JV, Friedman PJ. Radiologic errors in patients with lung cancer. West J Med. 1981; 134:485– 490. PMID: 7257363
- Donald J, Barnard SA.Common patterns in 558 diagnostic Radiology Errors.J Med Imaging Radi at Oncol.2012 ; 56(2):173-178. doi:10.1111/j.1754-9485.2012.02348.x
- Can Artificial Intelligence Reliably Report Chest X-Rays? Radiologist Validation of an Algorithm trained on 2.3 Million X-Rays. arXiv:1807.07455v2 [cs.CV] 4 Jun 2019
- Deep learning in chest radiography: Detection of findings and presence of change. Ramandeep SinghID1,2, Mannudeep K. Kalra1,2, Chayanin NitiwarangkulID1,2,3, John A. Patti1,2, Fatemeh Homayounieh1,2, Atul Padole1,2, Pooja Rao4, Preetham Putha4, Victorine V. Muse1,2, Amita Sharma1,2, Subba R. Digumarthy . PLOS ONE | https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204155 October 4, 2018
